
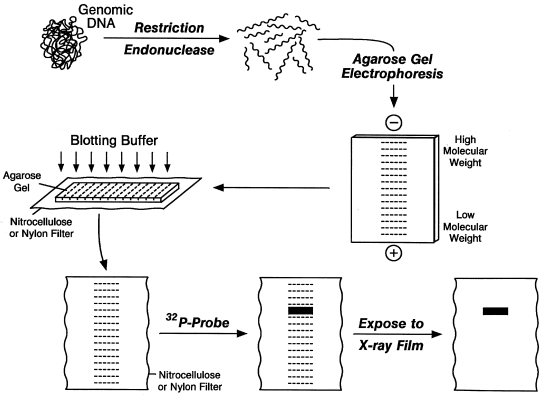
If the probe was labeled with radioactivity, it can expose X-ray film directly.īelow is an example of a real Southern blot used to detect the presence of a gene that was transformed into a mixed cell population. Southern blotting is a hybridization technique for identification of particular size of DNA from the mixture of other similar molecules. alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase).Ĥ) The location of the probe is revealed by incubating it with a colorless substrate that the attached enzyme converts to a colored product that can be seen or gives off light which will expose X-ray film. The DNA in the gel has been transferred (blotted) to a filter, then the filter is exposed. These may include determination of plasmid copy number in transfected cells. The presence of germline bands is interpreted only as a negative result. The probe cannot be seen but it is either radioactive or has an enzyme bound to it (e.g. The middle panel is a Southern Blot autoradiogram of the same gel. MDS will use standard Southern/Northern blot methods for a variety of applications. Last Updated on Tue, Molecular Pathology. This probe will form base pairs with its complementary DNA sequence and bind to form a double-stranded DNA molecule. This chapter describes a detailed protocol for genomic Southern blot analysis which can be used to detect transgene or endogenous gene sequences in cereal genomes. The DNA fragements retain the same pattern of separation they had on the gel.ģ) The blot is incubated with many copies of a probe which is single-stranded DNA. The DNA is denature into single strands by incubation with NaOH.Ģ) The DNA is transfered to a membrane which is a sheet of special blotting paper. Because there are so many different restriction fragments on the gel, it usually appears as a smear rather than discrete bands. 1) DNA (genomic or other source) is digested with a restriction enzyme and separated by gel electrophoresis, usually an agarose gel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
